2022.2.0 to 2023.0.0
1. Plugin Alias: Introduction of a New Alias Type
What changed
A new type of alias called "Plugin Alias" is now available. This alias represents server plugins provided by an operator, typically an Apache Maven repository. Each plugin you want to use with your system requires its own alias.
Why it matters
This allows better management and configuration of server plugins within your ADITO system, making plugin integration more structured and standardized.
Recommended actions
To create a Plugin Alias:
- Right-click on the
aliasfolder within your project. - Select a name for your alias.
- Choose the type
Plugin. - Configure the plugin this alias should represent by specifying its Maven coordinates: GroupId, ArtifactId, and pluginVersion.
Figure: Plugin Alias Type Selection
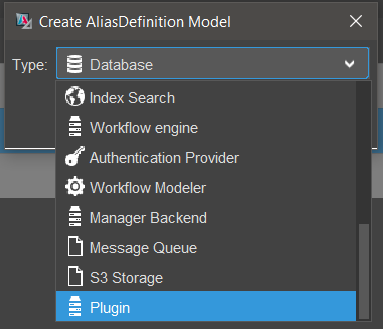
Figure: Plugin Alias Definition Configuration
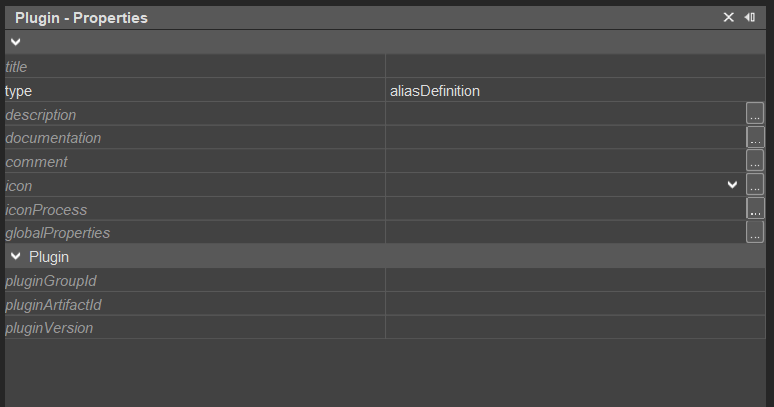
Example usage
The Exchange Webservices Plugin is identified by:
- pluginGroupId = de.adito.de.plugin
- pluginArtifactId = ews
- pluginVersion = 1.1.4
2. Manager Service Alias: Split into Two Separate Aliases
What changed
The existing Manager Service Alias has been split into two distinct aliases:
- Manager Backend Alias
- Message Queue Alias
This change was made because the message queue will now be used for additional tasks beyond the manager service.
Why it matters
Splitting these aliases clarifies their responsibilities and improves system modularity. Existing projects will be upgraded automatically to reflect this change.
Recommended actions
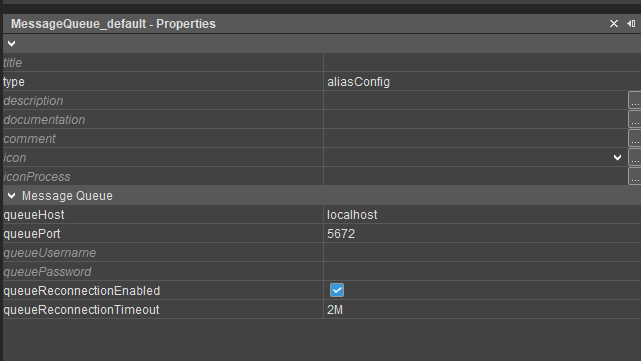
After upgrading, verify that your project contains both:
- Manager Backend Alias
- Message Queue Alias
Figure: Manager Backend Alias
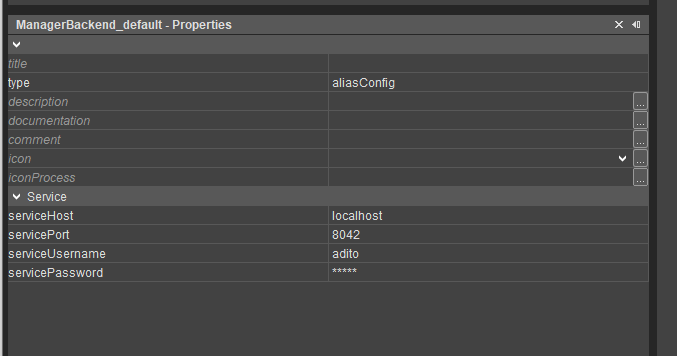
Figure: Message Queue Alias
3. Changed Default Sorting Behaviour for Read-Entity and Entity Webservices
What changed
From ADITO 2023.0.0 onward, Read-Entity (entities.getRows) and Entity Webservices do not apply sorting by default. This change improves performance and reduces loading times.
Why it matters
Sorting is often unnecessary and can degrade performance. Making sorting optional allows you to optimize data retrieval.
Recommended actions
If you need sorted data, explicitly add .applyRecordSorting() to your row configuration using constants:
entities.RECORD_SORTING_FULLto enable sortingentities.RECORD_SORTING_NONEto disable sorting
For entity webservices, add the query parameter applyRecordSorting with values "FULL" or "NONE".
Example usage
var loadConfig = entities.createConfigForLoadingRows()
.entity("Person_entity")
.fields(["#UID","LASTNAME"])
.applyRecordSorting(entities.RECORD_SORTING_FULL);
Example URL for an Entity Webservice on Person_entity (see module contact) with sorting enabled:
---
## 4. WorkflowModeler Authentication: Configuration of Flowable Admin Credentials
#### What changed
Starting with ADITO 2023.0.0, credentials for the Flowable admin can be configured within the workflow modeler alias of your systems. This enables opening the modeler directly from the ADITO client.
#### Why it matters
This streamlines access to the workflow modeler and centralizes credential management.
#### Recommended actions
Configure the Flowable admin credentials in the workflow modeler alias of your system. If using an ADITO SSP system, locate the Flowable admin password in the system's config map.
*Figure: Workflow Modeler Authentication Configuration*
