WWW-Authenticate Header
What is the WWW-Authenticate Header?
The WWW-Authenticate header is a standard HTTP response header used by servers to indicate the authentication methods that are supported when access to a resource is denied. It is most commonly included in responses with a 401 Unauthorized status code and informs the client how it should authenticate itself to gain access.
This header plays a key role in the challenge-response mechanism defined in HTTP authentication standards, allowing clients to understand which authentication schemes (e.g., Basic, Bearer, Digest) are expected and what parameters they must include in their follow-up requests.
Example:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm="ADITO_RESTentitywebservice"
Legacy Behavior (Before Version 2025.1)
Before version 2025.1, the WWW-Authenticate header was always statically set to:
WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm="ADITO_RESTentitywebservice"
This response was returned regardless of the authentication type configured for the webservice. It did not reflect the actual loginTypeId or any custom parameters, and the system did not support multiple headers or schemes.
Changes in Version 2025.1
Starting with version 2025.1, the behavior of the WWW-Authenticate header has been updated to be dynamic and RFC-compliant:
- The
auth-schemenow matches theloginTypeIdconfigured. - Multiple
WWW-Authenticateheaders can be returned if multiple login types are defined. - The Basic
realmcan now be overridden; otherwise, the legacy default value is used. - If no authentication configuration is found, no header is returned.
This change improves accuracy and compatibility with clients while preserving backward compatibility where needed.
Configuration in ADITO Entity Webservices
Overview
In ADITO, the behavior of the WWW-Authenticate header for entity-based REST webservices can be customized based on the authentication type defined in the process configuration. The system uses the loginTypeId to determine the appropriate authentication scheme and allows further customization via properties.
How to Configure
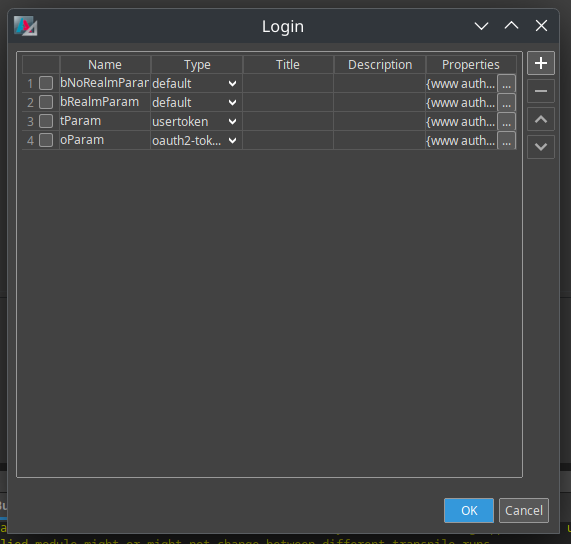
Figure: Overview of log levels for REST webservices.
-
Set the Login Type in the process configuration:
login→ Basicusertoken→ usertokenoauth2-token→ Bearer
-
Add Optional Parameters via the Properties tab:
- Key:
www authentication params - Value: comma-separated list of parameters (RFC-compliant), e.g.
realm="CustomRealm", version="1.0", info=public - Note: Quotation marks must be added manually if required by the syntax.
- Key:
-
Multiple Headers: If multiple login types are configured, the system may return multiple
WWW-Authenticateheaders, one for each. -
Fallback: If no login configuration is found, no
WWW-Authenticateheader is returned.
Special Case: Basic Authentication
- If a
realmparameter is explicitly configured, it will be used. - If no
realmis set, the system defaults to:ADITO_RESTentitywebserviceorADITO_RESTentityformwebservice
Example Output
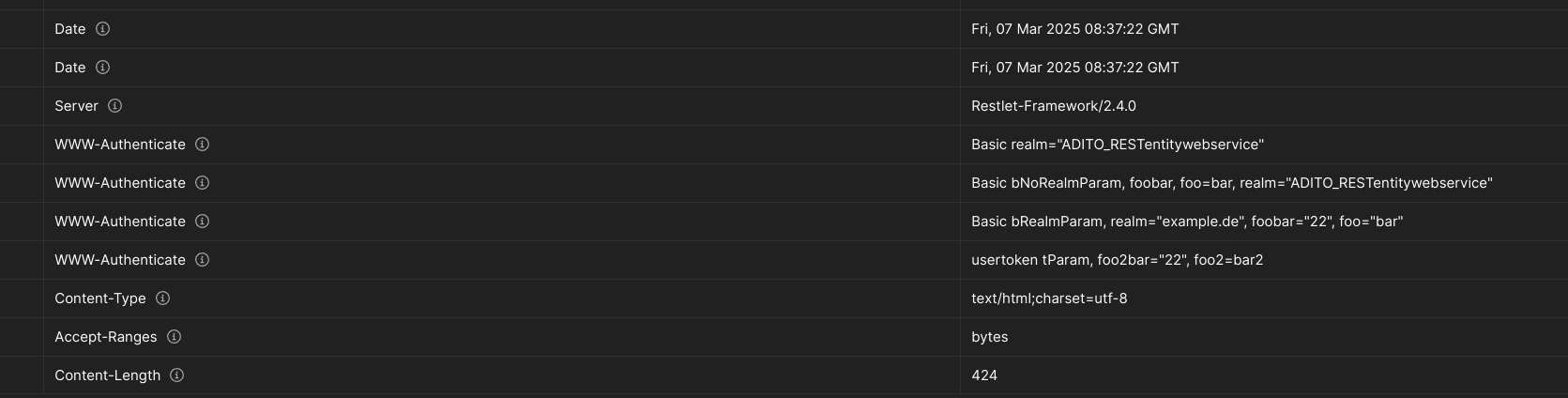
Figure: Response with 4 different www-authentication header.
Best Practices and Considerations
- Always ensure parameter values are RFC 9110-compliant.
- When customizing, test with various clients to ensure headers are parsed correctly.
- Use descriptive
realmvalues for Basic authentication to guide clients. - If no authentication is expected, avoid returning this header at all.