Logging for REST Webservices
This document outlines the logging mechanisms implemented for REST webservices, designed to assist developers by providing detailed and structured log and error messages. Two primary log levels/debug flags have been introduced: REST_WEBSERVICES and REST_WEBSERVICES_EXTENDED.
Log Levels Overview
REST_WEBSERVICES
The REST_WEBSERVICES log level captures essential information about incoming webservice requests and their corresponding responses. This includes:
- Incoming Request Logging: Records the name of the webservice invoked, the HTTP method used (e.g., GET, POST), and the user initiating the request.
- Request Duration Logging: Measures and logs the time taken to process each request, enabling performance monitoring and troubleshooting.
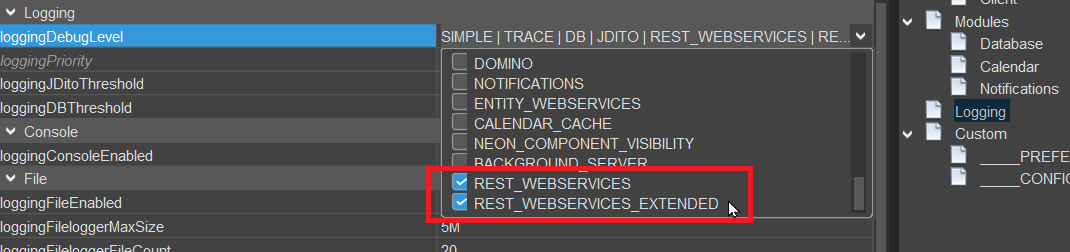
Figure: Overview of log levels for REST webservices.
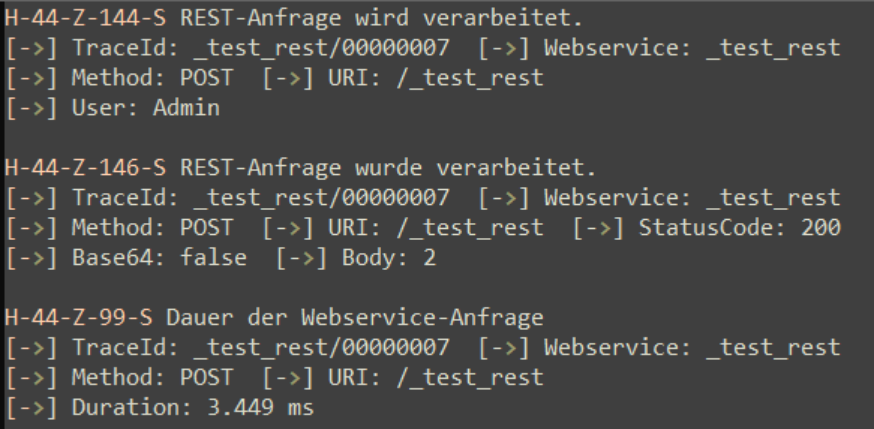
Figure: Example of request duration logged for REST webservices.
REST_WEBSERVICES_EXTENDED
The REST_WEBSERVICES_EXTENDED log level extends the capabilities of REST_WEBSERVICES by additionally logging the request and response payloads as JSON objects. This enhanced detail facilitates in-depth debugging and analysis.
Sensitive information such as login credentials is excluded from the logs to maintain security and privacy.
ENTITY_WEBSERVICES
The ENTITY_WEBSERVICES log level operates similarly to REST_WEBSERVICES, but it is specifically tailored for Entity webservices, providing analogous logging details for entity-related operations.
TraceID Usage
All log and error messages generated under these log levels include a TraceID. The TraceID serves as a unique identifier that correlates log entries with the corresponding webservice request and response, streamlining the process of tracing and diagnosing issues.
TraceID Format
The TraceID follows the format:
<webservice-name>/<hex-id>
Example:
Person_webservice/0200FC21
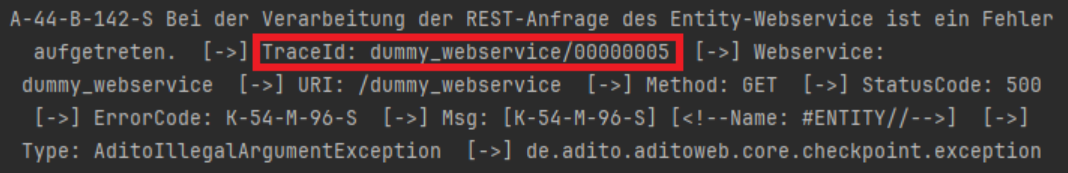
Figure: Log entry displaying the TraceID for request correlation.
TraceID in Responses
In addition to logging, the TraceID is included in the HTTP response headers under the key X-adito-trace. This inclusion allows clients to reference the TraceID for support or troubleshooting purposes.
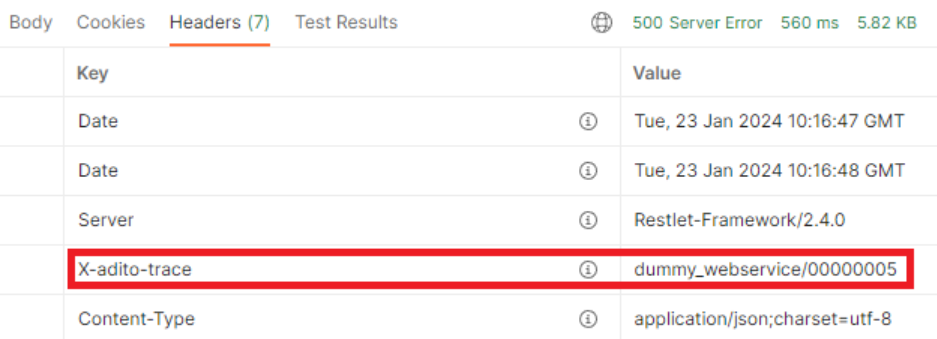
Figure: HTTP response header containing the TraceID.
Utilizing the TraceID enables efficient correlation between client-side interactions and server-side logs, greatly simplifying debugging and monitoring tasks.