Multi-Tenancy
Overview
The ADITO platform supports multi-tenancy by design. Each tenant can only access the portion of the data that has been explicitly authorized. This ensures secure, isolated access within shared or separated infrastructure scenarios.
For the ADITO Appliance operating model, all system and application data is stored in a database management system (DBMS) provided and managed externally by the customer.
Tenancy Model A: Application-Level Separation
This model is supported by both the ADITO Cloud and ADITO Appliance deployment models.
A central ADITO application runs per deployment environment. It uses a shared system and data database. Tenant-specific access is enforced via roles and permissions.
During client session startup, the application registers the tenant ID associated with the authenticated user. Based on this, access is restricted to those objects (entities, fields, actions, etc.) and records authorized for that tenant.
This setup provides a consistent application structure and minimizes effort when applying changes that affect all tenants.
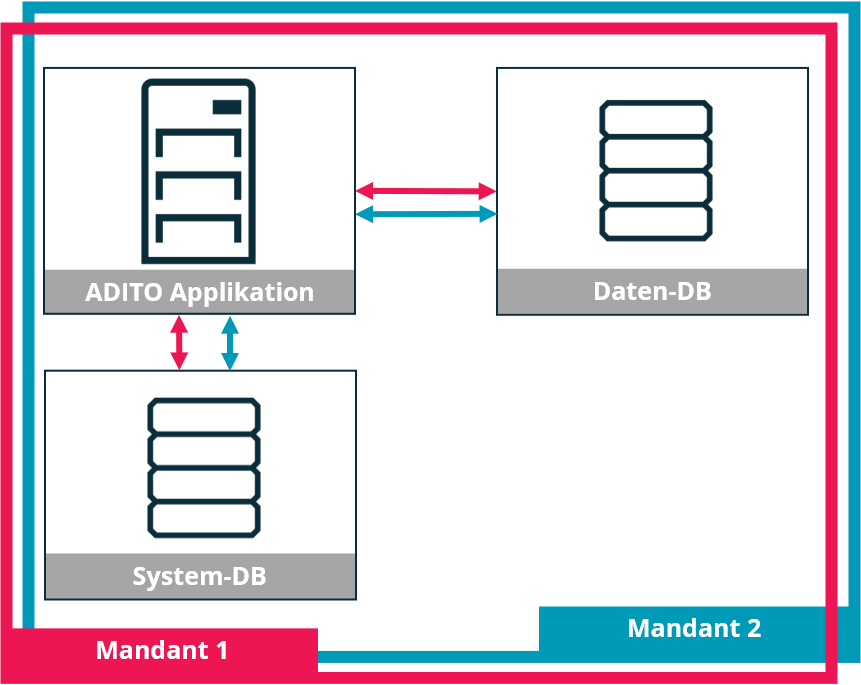
Figure: Application-level tenant separation
Tenancy Model B: Data-Level Separation
This model is supported only by the ADITO Appliance deployment model.
Each deployment environment runs a central ADITO application with a shared system database. However, each tenant is assigned a dedicated data database. This setup is structurally similar to Model A but separates tenant data at the database level.
This model offers reduced risk compared to relying solely on application-level permissions. However, shared data access for cross-tenant reporting or queries is not possible.
Example:
2 tenants, 4 deployment environments (DEV, TEST, STAGING, PROD)
→ 1 stage per environment with 2 dedicated data databases
→ Total: 4 stages, 4 system databases, 8 data databases
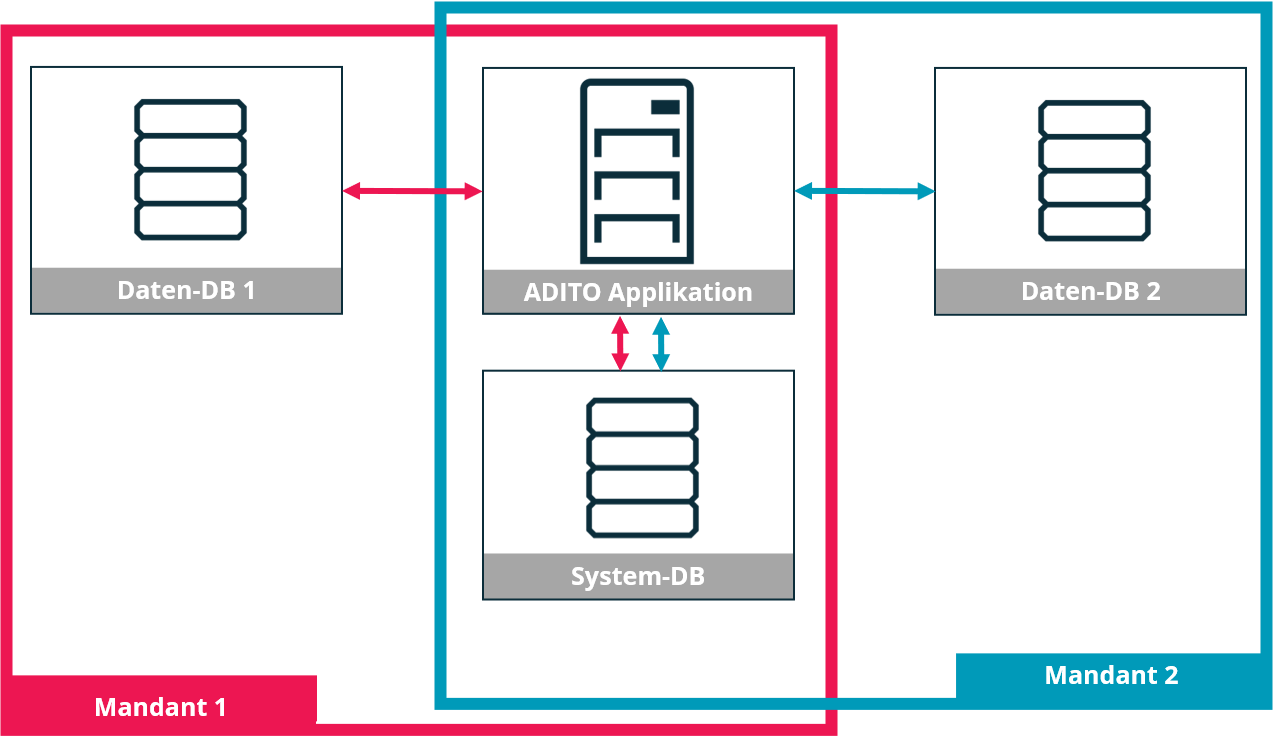
Figure: Data-level tenant separation
Tenancy Model C: Environment-Level Separation
This model is supported only by the ADITO Appliance deployment model.
In this setup, each tenant receives a separate ADITO application instance per deployment environment. Each application instance maintains its own system database, while a shared data database is used across all tenants in the same environment.
Tenants access a common dataset, and authorization is managed by each ADITO application. This approach enables isolated application configurations per tenant. However, updates or adjustments must be applied individually to each instance.
Operating multiple ADITO applications requires more administrative effort and hardware resources.
Example:
2 tenants, 4 deployment environments (DEV, TEST, STAGING, PROD)
→ 2 stages per environment with 1 shared data database
→ Total: 8 stages, 8 system databases, 4 data databases
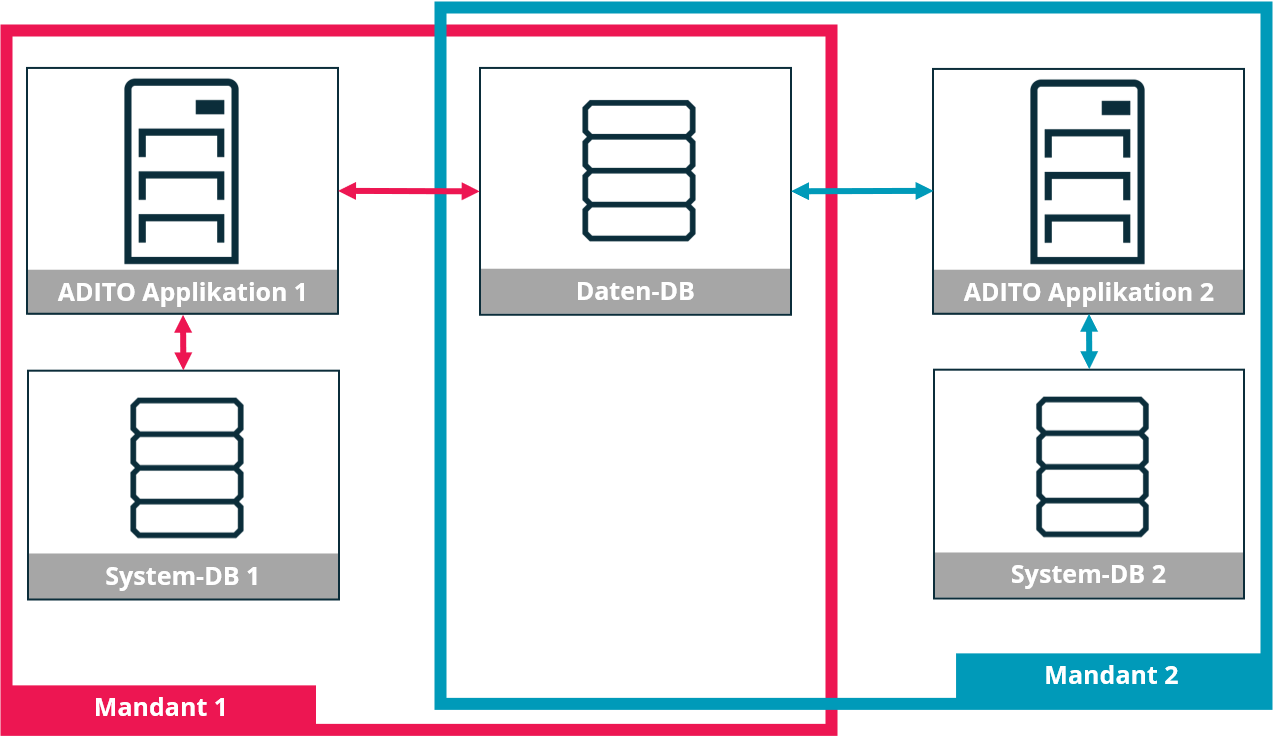
Figure: Environment-level tenant separation