Customization
Introduction
ADITO offers a flexible platform that supports both low-code customization and full-code development. This section outlines the differences, use cases, and interplay between configuration via UI tools and advanced extensions via code.
Understanding this distinction helps teams choose the right approach for each requirement.
Customization (Low-Code)
Customization refers to configuration-based changes using ADITO-provided tools and interfaces without writing Java code.
Typical Tools
- App Designer: Create and configure views, dashboards, field behavior, and layout.
- ADITO Designer: Define entities, relationships, permissions, and metadata models.
- Business Rules & JDito: Add logic using ADITO's scripting language.
Characteristics
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed | Fast to implement and test |
| Update-friendly | Less sensitive to version upgrades |
| Accessible | Can be done by trained consultants or key users |
| Versioned | Managed via ADITO GitLab server (project export/import supported) |
Use customization for UI design, form logic, entity configuration, and most automation rules.
Development (High-Code)
Development refers to writing code outside the standard configuration interface to implement advanced or custom behavior.
Typical Tools
- Java Plugin SDK: Extend backend behavior with custom services or data
- External Integrations: Build REST clients or consume APIs in plugins
Use Cases
- Complex data processing or calculations
- External system integration (e.g. SAP, Exchange)
- Custom authentication mechanisms
Plugins are developed in Java and deployed to the ADITO platform through the server environment.
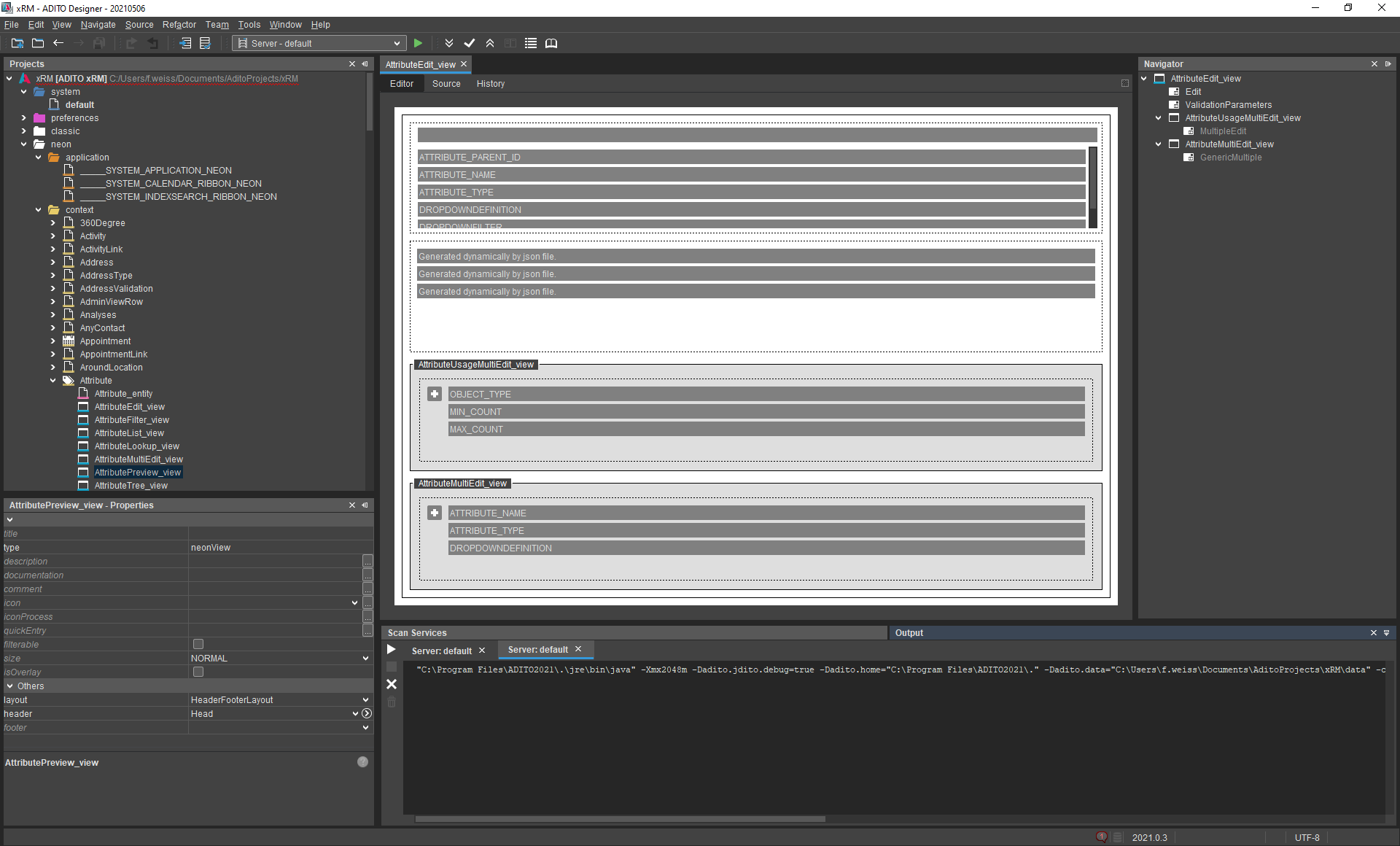
The ADITO Designer
ADITO Designer
Der ADITO Designer ist die ADITO-eigene modulare Entwicklungsumgebung, mit dem Anpassungen an ADITO (sog. Customizing) vorgenommen werden. Mittels verschiedener Editoren werden bspw. Masken, Prozesse, Reports oder Schnittstellen weiterentwickelt. Das ADITO Projekt wird für die Weiterentwicklung in eine lokale Projektstruktur übernommen, die der Designer verwaltet. Änderungen werden mittels Deploy in die Systemdatenbank übertragen.
The ADITO Designer is the core tool for both customizing and preparing projects for extension. It is based on Apache NetBeans and manages the local project structure.
Features
- Create and edit entities, fields, views, roles
- Manage workflows, processes, and data mappings
- Define scripts and rules using JDito (JavaScript-based)
- Deploy changes to the live system
JDITO
As the programming language for customizing, ADITO uses its proprietary scripting language JDito. JDito is based on JavaScript extends its functionality with system modules that provide ADITO-specific methods.
Combined Workflow
Often, both approaches are used in the same project:
UI Forms and Views → App Designer (Customization)
Business Logic → JDito (Customization)
Advanced Backend Logic → Java Plugin (Development)
External API Integration → REST/Plugin (Development)
Use customization where possible and fallback to development where needed.