JDito System Modules and System Variables
System Modules
In JDito, all extended functionalities beyond basic JavaScript capabilities are provided through system modules. Each module groups methods and constants that pertain to a specific topic or domain.
Purpose and Use of Modules
A module typically contains all methods and constants related to its domain. For instance, system.calendar includes all functions used to interact with calendar entries, while system.db provides interfaces for database operations.
Constants act as readable aliases for cryptic values to improve code clarity. For example, instead of using the numeric value 7 to identify Apache Derby as a database type, JDito provides the constant db.DBTYPE_DERBY10 for better readability.
Methods allow developers to control the ADITO system — for example, by querying a database or updating a UI component. These methods are not to be confused with JDito functions, which are defined by users and consist of ordered JavaScript instructions. JDito methods, by contrast, are implemented in the interpreter and provide access to core ADITO functionalities.
To use any module, it must be imported at the beginning of the JDito process.
The import statements must always appear at the very top of a process. If placed elsewhere, an error will occur.
Import Example
import { result } from "@aditosoftware/jdito-types";
// Code begins here
result.string("My result");
Available System Modules
JDito provides a variety of system modules, each grouping methods and constants by topic. These modules must be imported explicitly and offer access to the core ADITO platform functionalities.
| System Module | Description |
|---|---|
system.ACTION | Contains only constants representing client actions, e.g., ACTION.FRAME_CREATE, ACTION.FRAME_EDIT. |
system.ALIAS | Contains only constants used to reference keys within alias objects, such as ALIAS.CHARSET, ALIAS.PASSWORD. |
system.SQLTYPES | Provides constants for SQL column types and validation methods, e.g., SQLTYPES.isTextType(SQLTYPES.CHAR). |
system.calendars | Groups all methods and constants for working with calendars and calendar entries. |
system.cti | Contains methods and constants for integrating with telephone systems. |
system.datetime | Includes methods and constants for handling dates, timestamps, and time zones. |
system.db | Provides methods and constants for interacting with databases: SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, etc. |
system.eMath | Offers safe arithmetic operations (add, subtract, multiply, divide, round) on String-based numbers. Supports both integer and decimal operations, along with rounding constants. |
system.fileIO | Methods and constants for server-side file input/output operations. |
system.gantt | Currently contains no functionality. |
system.im | Methods and constants for the XMPP backend (instant messaging). |
system.imClient | Methods and constants for the XMPP client. |
system.indexsearch | Contains methods and constants for indexing and searching with Solr. |
system.logging | Provides logging functionality. |
system.mail | Methods and constants for sending emails and handling email objects. |
system.neon | Methods and constants for controlling the Neon web client. |
system.neonTools | Provides helper methods for managing the Neon client. |
system.net | Allows REST/SOAP web service calls, URL validation, and retrieval of URL contents. |
system.notification | Methods and constants for working with the ADITO notification system. |
system.pack | Methods and constants for ZIP archive operations. |
system.plugin | Enables calling ADITO plugins on the server side. |
system.process | Provides methods and constants for executing JDito processes immediately or on schedule. |
system.project | Methods and constants for accessing deployed project models, such as getAlias(), getDatamodel(), getInstanceConfigValue(). |
system.question | Displays modal dialogs using methods and constants. |
system.report | Interfaces with the ADITO reporting engine. |
system.result | Methods for returning values to the ADITO core (used in value or display processes). |
system.text | Methods for working with multi-string encoding/decoding, text formatting, parsing, and hashing. |
system.tools | Despite its name, this module handles user and role management. |
system.translate | Provides access to the ADITO translation subsystem. |
system.treetable | Currently contains no functionality. |
system.util | Utility functions such as BASE64 encoding/decoding and UUID generation via getNewUUID(). |
system.vars | Methods for reading and setting variable values (component, field, system, local, image). |
System Variables
System variables are containers for values provided by the ADITO core or defined within JDito code. They are always prefixed with $ and accessed via the system.vars module using vars.get() or vars.set().
// Reading a variable
vars.get("$sys.operatingstate");
vars.get("$field.UUID");
vars.get("$local.value");
// Setting a variable
vars.set("$context.calculatedVal", calcValue);
vars.set("$field.COUNTRY", myCountry);
The method vars.getString() is no longer required, even for reading string values. This method will be marked as deprecated in future ADITO versions.
System variables can only be read and written within the context in which they were created.
It is not possible to set a variable from one context (e.g., “Organisation opened in tab 1”) and access it from another (e.g., “Organisation opened in tab 2”).
As a result, using global variables as caching mechanisms is highly limited, because cache invalidation is difficult to control. Typically, invalidation occurs:
- After a user re-login, handled in the
autostartNeonprocess, or - Via a designated ServiceImplementation configured for the process.
There are several types of system variables, not only $sys variables. In the following, you can find a description of important system variables.
$local Variables
$local variables exist for the duration of a user’s session (per login). The persistence of these variables on the server depends on the configuration of the corresponding server process, which must always be executed under a specific user.
For instance, in the autostartNeon process, various $local variables are initialized that are later required by the client. $local system variables are only visible within specific JDito processes. They are primarily set by the ADITO core to pass contextual values into those processes.
A common example is the process_audit process, which reacts to dataset audit events. Information about affected database columns, their types, and their old and new values are passed as $local variables and can be accessed through the system.vars module:
// Reading a local variable
var action = vars.get("$local.action");
// Setting a local variable
vars.set("$local.taskId", "1234-1234-1234");
As for the server, this means:
When configuring the interval of a server process, it is possible to define whether the JDito instance should be retained:
- If yes, then the global variable persists across multiple executions — on the same server pod (e.g.,
adito-web-bg-0), i.e., the software-side instance of an ADITO server. - If no, then the global variable is reinitialized for each new execution and must be set again.
Overview of $local Variables
Maintaining a complete and up-to-date documentation of all $local variables — including their availability and usage across every possible context — would be highly complex and difficult to maintain.
Instead, use the Designer’s debugger to inspect currently available $local variables. When the debugger is active, a window labeled "Debugger" shows all variables relevant to the process context where the current breakpoint is located.
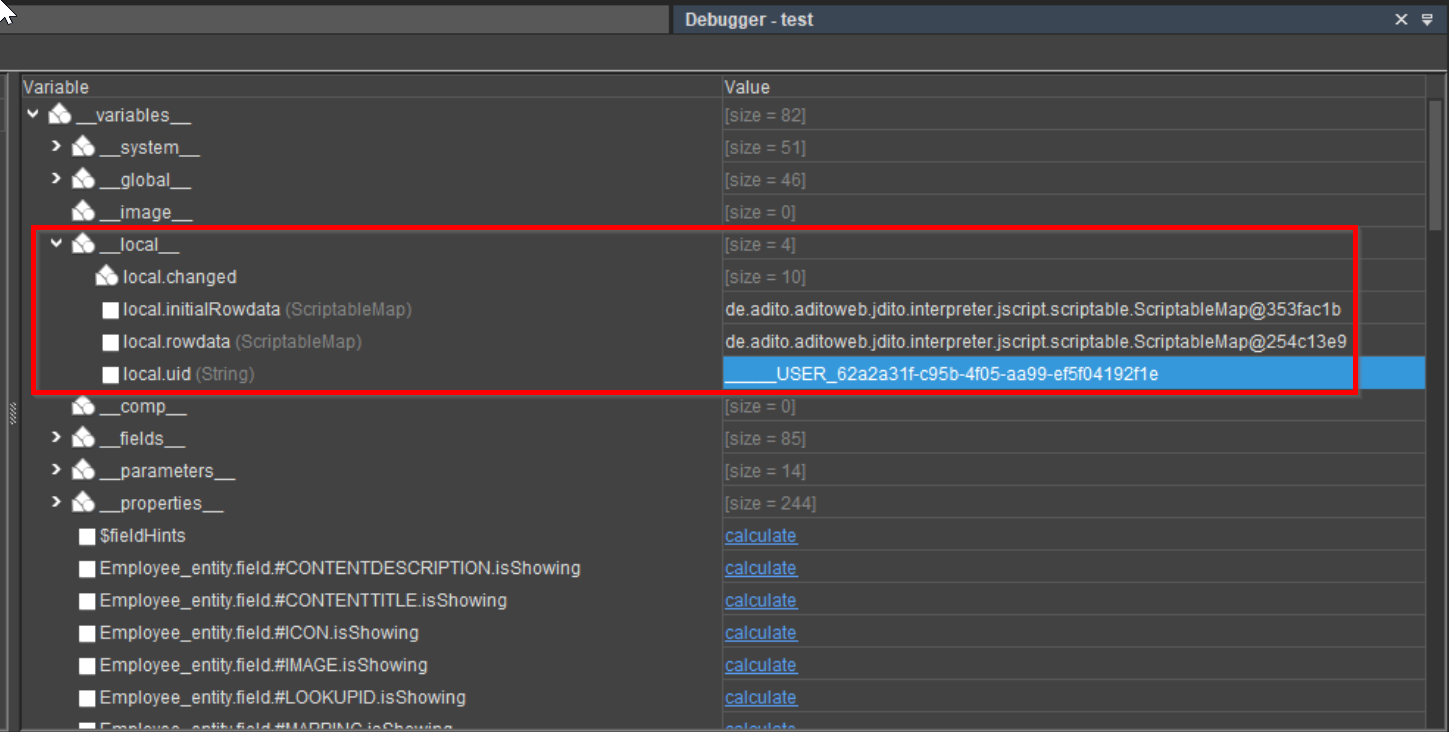 Figure: Inspection of
Figure: Inspection of $local variables via the Designer Debugger.
For more information on the debugger, consult the Designer Manual (PDF).
The below list does not include $local variables that are explained in other chapters of this documentation. For example:
$local.operator2→ see chapter FilterExtension$local.value→ see chapter Accessing the value of an EntityField
When searching this document for $local variables using full-text search, be aware that for formatting reasons, some variable names may include line breaks.
As a result, variables like $local.initialRowdata may only be found by searching for initialRowdata.
This list is neither complete nor exhaustive.
It includes only typical examples. Many $local variables may have different meanings in different processes.
Selected $local Variables
Name: $local... | Examples of Return Value | Data Type | Examples of Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
condition | Filter condition, e.g., "CONTACT.STATUS is null" | String | filterConditionProcess of a FilterExtension; groupQueryProcess of a FilterExtensionSet |
filter | Filter configuration (see below) | object | contentProcess of a jDitoRecordContainer |
idvalue | IDs affected by a change in an indexRecordContainer | object | affectedIds process of an indexRecordContainer (see chapter “Index for Global Search”) |
idvalues | ID affected by a change in a jDitoRecordContainer | String | contentProcess of a jDitoRecordContainer |
initialRowdata | Initial values of an Entity dataset (before user changes) | object (EntityField name → initial value) | onDBUpdate process of a dbRecordContainer |
lookupFieldName | See below | String | Used in FilterExtensionSet for Attributes |
rawvalue | User input (e.g., selected item in combo box) | String | filterConditionProcess of a FilterExtension |
rowdata | Entity dataset values after user changes | object (EntityField name → value) | onDBDelete |
uid | Record identifier in a dbRecordContainer | String | onDBInsert, onDBUpdate, onDBDelete |
$local.filter
This variable provides the filter configuration used within a context such as a jDitoRecordContainer. Its structure is shown below.
// if a filter is set, it looks like this:
{
"filter": {
"type": "group",
"operator": "AND",
"childs": [
{
"type": "row",
"name": "ACTIVE",
"operator": "EQUAL",
"value": "Ja",
"key": "true",
"contenttype": "TEXT"
}
]
},
"permissions": null,
"subset": null,
"ids": null
}
// if a filter is NOT set, it looks like this:
{
"filter": null,
"permissions": null,
"subset": null,
"ids": null
}
$local.lookupFieldName
Availability:
This variable is available in the valueProcess of a Parameter within a Consumer.
Content:
- If the Consumer is connected to an EntityField (i.e., lookup field), the variable contains the name of that EntityField.
- If used in FilterExtensions or FilterExtensionSets where a Consumer provides the values, the variable contains the name of the FilterExtensionField.
Example Use Case in xRM:
In a FilterExtensionSet for Attributes, some FilterExtensionFields use a Consumer to provide selectable values. To identify which FilterExtensionField triggered the process, the system uses:
vars.get("$local.lookupFieldName");
This allows the Consumer to react dynamically based on the selected FilterExtensionField.
$sys Variables
$sys variables are visible within a single client session and are independent of any specific context. They are typically used to store values required throughout the client, such as configuration parameters or access control via sales areas.
// Getting a sys variable
var action = vars.get("$sys.useRights");
// Setting a sys variable
// Only possible if SALESAREA is a dynamic user property
vars.set("$sys.salesArea", tools.getCurrentUser()[tools.PARAMS]["SALESAREA"]);
Overview of $sys Variables
The following table provides a detailed overview of most of the available $sys variables in ADITO. These variables are accessible within the client context and can be used to retrieve system, session, UI, and user-related information.
Name ($sys....) | Description of Return Value |
|---|---|
activeimage | Internal ID of the active top image (entity, report, mail) |
activewindow | Internal ID of the active frame |
ancestorimageuid | ID of all currently opened frames |
calenderusers | Calendar users |
clientcountry | Country of the client |
clientdata | DATA directory of the client (visible via $ADITO_DATA) |
clienthome | HOME directory of the client |
clientid | ID of the client |
clientlanguage | Language of the client |
clientlocale | Localisation of the client (e.g., de_DE) |
clientos | Operating system of the client |
clienttemp | Temp directory of the client |
clientuid | UID of the client |
clientvariant | Language variant of the client |
clientversion | Version of the client (e.g., 2021.0.1) |
content | ID of the currently selected record |
currentcontextname | Name of the current context |
currententityname | Name of the current entity |
currentimage | ID of the current image variable |
currentimagename | Name of the current image variable |
currentimagetype | Type of the current image variable |
datarow | Condition of the current record (excluding WHERE) |
datarowcount | Number of datasets loaded in the RecordContainer (considering filters and limit via maximumDbRows) |
datarowcountfull | Total number of datasets available via the RecordContainer, ignoring maximumDbRows limit |
date | System date as long |
dbalias | Active database alias |
dynamicdate | System date as long |
extendedpattern | Pattern as executed |
filter | Current selection filter object with properties: .filter, .permission, .filterCondition, .condition |
filterable | Boolean indicating whether the current view is filterable |
groupable | Boolean indicating whether the current view is groupable |
groups | Currently active groups |
hasSelection | Boolean indicating whether a selection is used |
licenseid | ID of the license |
operatingstate | Current operating state of the entity/view |
order | Current record sort order |
origin | Origin of the URL |
outsidelineaccess | Area code of the provider (CTI) |
pageable | Boolean indicating whether the RecordContainer is pageable |
parententity | Name of the parent entity (for dependencies) |
parentuid | UID of the parent entity (for dependencies) |
pattern | Current pattern as entered |
pendingpattern | Next pattern that will be executed |
preferencesid | ID of the selected preferences (if multiple choices exist) |
presentationmode | Current state of the view/entity |
recordstate | State of the current record in the view/entity |
scope | Scope of the client |
selection | Current selection (for entity or index) |
selectionRows | All rows in the current selection |
selections | Multistring array with the following structure:[0] Static: Used to open context[1] Designer: Defined in Designer[2] Search mask: User input[3] Dependency: Linked record[4] Extra: Global search |
serveraddress | Server URL address |
serverdata | DATA directory of the server |
serverhome | HOME directory of the server |
serverid | ID of the current system |
serveros | Operating system of the server |
serverport | Port(s) used by the current server |
servertemp | TEMP directory of the server |
serverversion | Server version |
staticdate | Current date (static) as long |
staticmillis | Current timestamp in milliseconds |
superframe | Name of the upper frame |
superframeid | ID of the upper frame |
superimage | Name of the upper image |
superimageid | ID of the upper image |
superimagetype | Type of the upper image |
superwindowid | ID of the upper window |
tablescanbecreated | Boolean indicating whether new records can be created in this context |
tablescanbedeleted | Boolean indicating whether records can be deleted in this context |
tablescanbeedited | Boolean indicating whether records can be edited in this context |
tableselection | Condition applied to the selected table |
tableviewselection | Structured condition of the current table view |
timezone | Time zone of the current user |
today | Current day (without time) as long |
uid | UID of the current record |
uidcolumn | Name of the UID column in the record |
user | Username of the current user |
useridletime | Idle time of the current user |
usertoken | Token of the current user |
validationerrors | String containing current validation errors |
viewmode | View mode of the current component |
workingmode | Current working mode |
workingmodebeforesave | Working mode before the last save action |
$field Variables
$field variables correspond to $comp variables in the ADITO Legacy platform but are used exclusively within the Neon Entity environment. They represent the values of specific EntityField objects.
Via the system.vars module, an EntityField value can only be read vars.get(). vars.set() does not work in this case. To modify an EntityField, use the appropriate method provided by the system.neon module.
Examples:
// Reading an EntityField value
var id = vars.get("$field.UUID");
// Setting an EntityField value
neon.setFieldValue("$field.MYENTITYFIELD", myValue);
$context Variables
$context variables are available only during the lifetime of a context, such as a Neon data model opened in a MainView.
They are temporary and scoped to that specific context, allowing you to store and access values relevant to the currently opened entity or view.
Examples:
// Reading a context variable
var oldObjectType = vars.get("$context.originalObjectType");
// Setting a context variable
vars.set("$context.PushDataPrivacyNotification", "true");
$cluster Variables
$cluster variables are visible to all clients and are maintained by the server.
They are commonly used as shared caches or for storing global values that must remain consistent across the entire system, regardless of which client accesses them.
They are accessed using the same methods as $sys variables.
Example
// Getting a cluster variable
var supportEmail = vars.get("$cluster.supportMail");
// Setting a cluster variable
vars.set("$cluster.supportMail", "support@adito.de");