Adding Tasks
Introduction
Instead of creating a new task in the xRM Context "Task" (module task) (and connecting it manually with a Contact, a Company, an Opportunity, etc.) you can also create a task directly in certain Contexts that should be connected with the task. Usually, this is done via an Action that is available via the three dot button in the CardViewTemplate of the PreviewView. Here is an Example from Context "Organisation" (module contact):
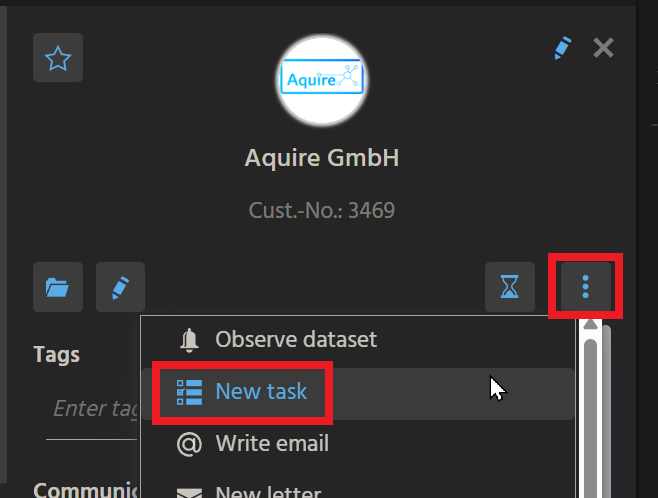
Action "New task" in the CardViewTemplate of OrganisationPreview_view (module contact).
In the MainView, there is a tab titled "Tasks" (e.g., in CampaignMain_view):
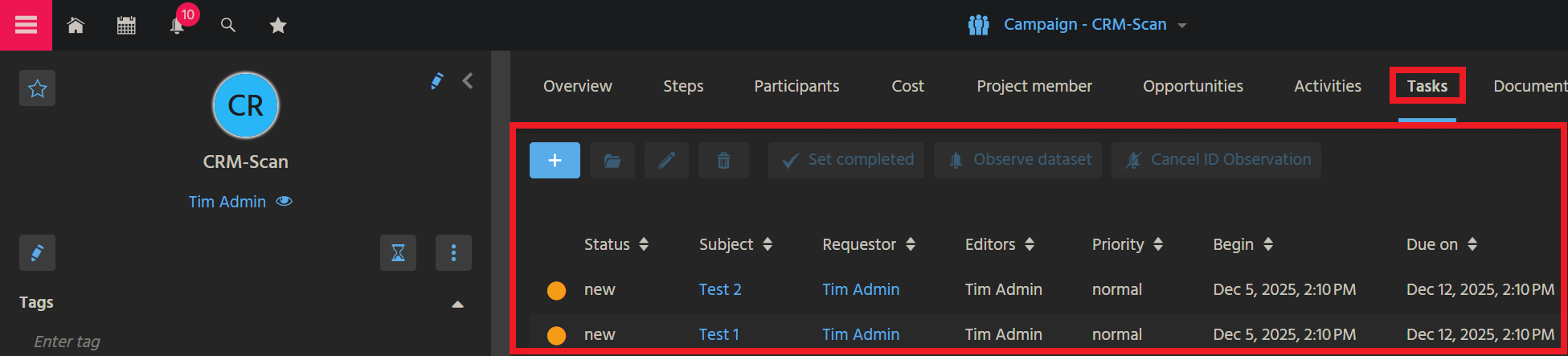
Tab "Tasks" in CampaignMain_view (module campaign)
This chapter explains how to add "Task" functionality to a Context, using the example of Context "Organisation" (module contact).
Step by step instructions
These are the steps to add a similar "New task" functionality to the PreviewView of a Context:
For training purposes, you may perform these steps using an xRM Entity that has got no "New task" Action yet - e.g., BulkMail_entity (module bulkmail).
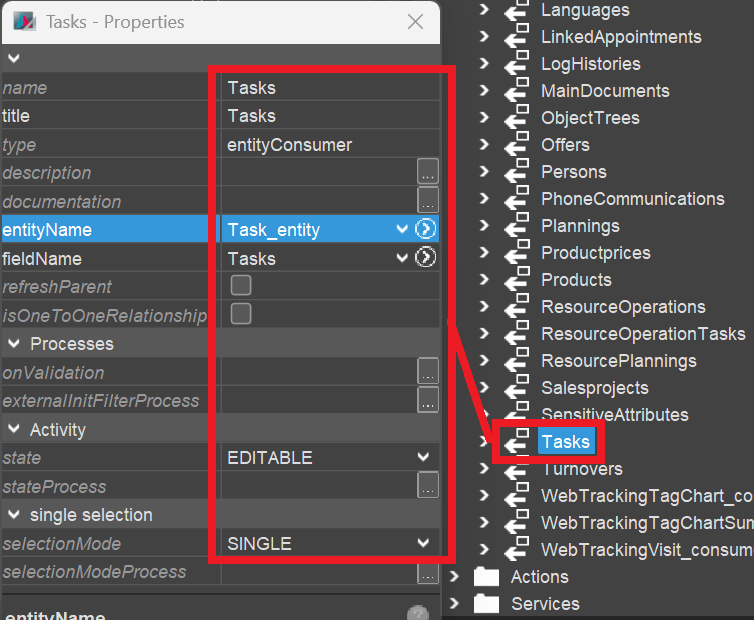
Create Consumer of Provider "Tasks"
Create a Consumer named and titled "Tasks" and connect it with Provider "Tasks" of Task_entity - cf., e.g., Organisation_entity (module contact):
Configure "Tasks" Parameters
In the Navigator window, unfold Consumer "Tasks" and set its Parameters Objectid_param and RowId_param. Again, you can use Organisation_entity (module contact) as pattern:
import { result } from "@aditosoftware/jdito-types";
import { ContextUtils } from "ContextUtils_lib";
result.string(ContextUtils.getCurrentContextId());
import { result, vars } from "@aditosoftware/jdito-types";
result.string(vars.get("$field.CONTACTID"));
(Replace CONTACTID by the EntityField that is related to your own Context's primary key.)
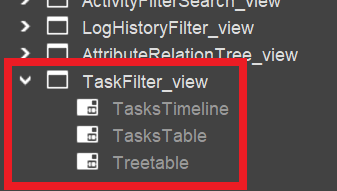
Assign View reference
In the Context's MainView, add a View reference to TaskFilter_view, which will add a tab named "Tasks":
Create Action "newTask"
Create Action "newTask" - again, you may use, e.g., Organisation_entity (module contact) as pattern:
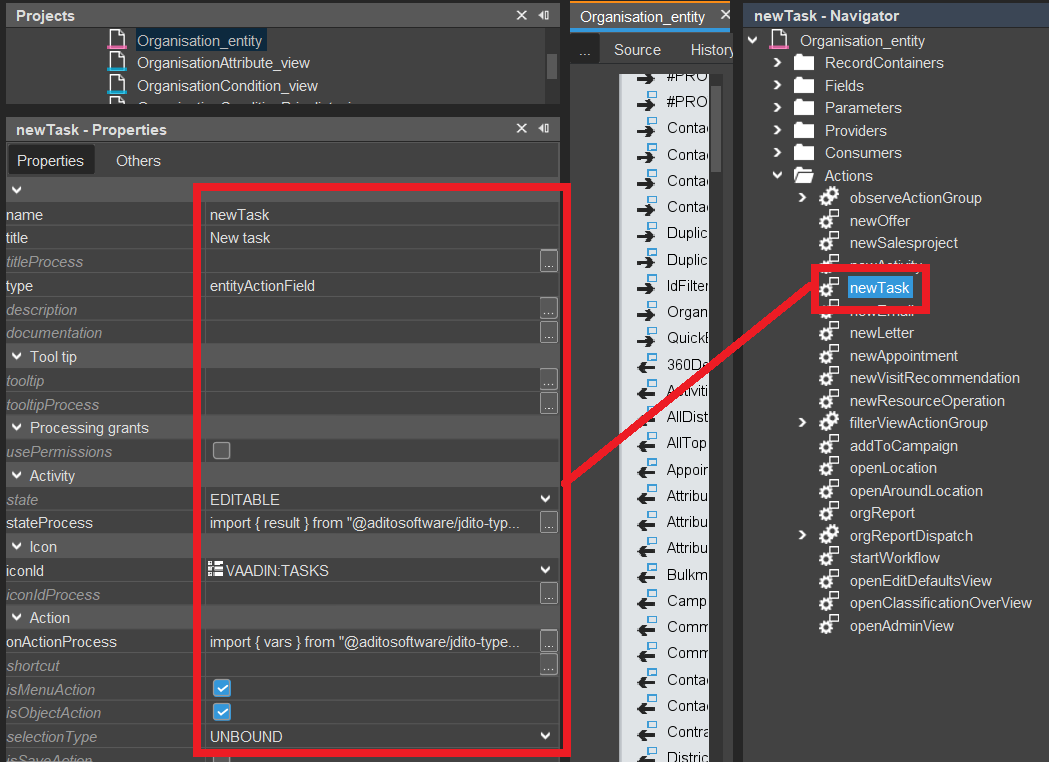
The stateProcess needs to make sure that the Action is disabled for inactive records:
import { neon, result, vars } from "@aditosoftware/jdito-types";
import { $ContactManagementKeywords } from "ContactManagementKeywords_registry";
if(vars.get("$sys.viewmode") != neon.FRAME_VIEWMODE_TABLE)
{
if (vars.get("$field.STATUS") == $ContactManagementKeywords.contactStatus$inactive())
{
result.string(neon.COMPONENTSTATE_DISABLED);
}
}
(Replace these status-related Keywords by the respective status-related Keywords of your own Context.)
The onActionProcess can be kept quite simple:
import { vars } from "@aditosoftware/jdito-types";
import { TaskUtils } from "Task_lib";
TaskUtils.createNewTask(vars.get("$field.CONTACTID"));
(Replace CONTACTID by the EntityField that is related to your own Context's primary key.)
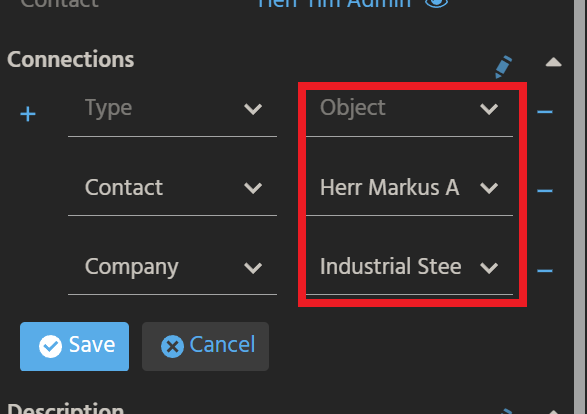
Availability in "Connections" ViewTemplate
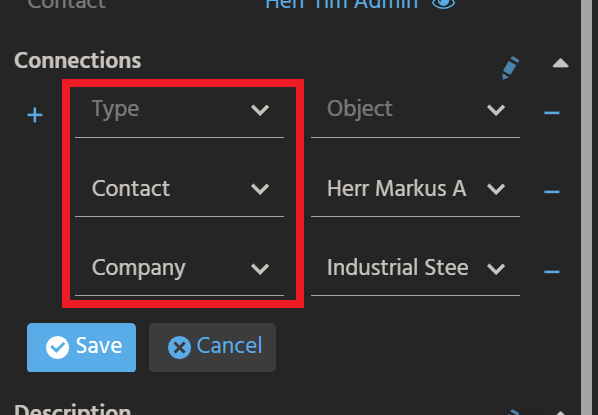
The PreviewView of Context "Task" includes an editable ViewTemplate labelled "Connections", which shows a list of connected records, along with the respective Context's title.

For showing the related record(s) of your Context here, and for adding further connections to your Context's records, the following steps are required:
Create Consumer for Object_entity
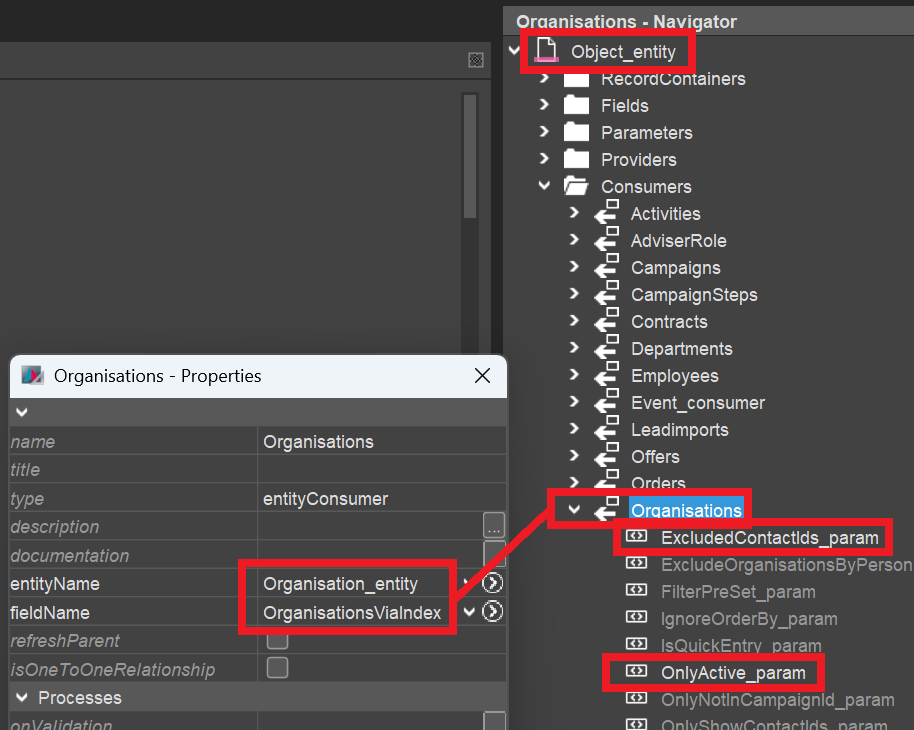
Navigate to Object_entity (module root), create a Consumer named like the plural of your Context name (e.g., "Organisations") and connect it to a suitable Provider (usually having a similar name as the Consumer) of your Context.
If there is no such Provider yet, then create it, name and title it like the Consumer, expose it, and create all Parameters required for retrieving the respective dataset(s) in the RecordContainer.
Then, in the Consumer, fill the required properties of all relevant Parameters. (Usually, there should be at least a Parameter, in whose valueProcess you specify the primary key of the dataset connected to the task.)
Here is an example for Context "Organisation" (module contact):
Extend getContexts
In ContextUtils_lib (module root), you can find a method named ContextUtils.getContexts, which returns the names of all Contexts that should be selectable in the left part of the "Connections" ViewTemplate:
Now, make sure your Context's name is included in the whitelist of method ContextUtils.getContexts. When using modularization, you will do this via a ServiceImplementation. Then, the Transpiler will automatically generate the required function (returning the Context name(s)) in ContextUtils_lib (module root) ...
function _____GENERATED_contextSelectionList_service_cm_impl()
{
//@ts-ignore
return [
"Organisation",
"Person",
"PrivatePerson"
];
}
...and add this function to the array contextServices, which will subsequently be looped over, in order to fill the whitelist. (See screenshot below.)
However, for testing purposes (when using an unmodularized project), you may simply add your Context's name manually to the whitelist:
whitelist.add("MyContextName");
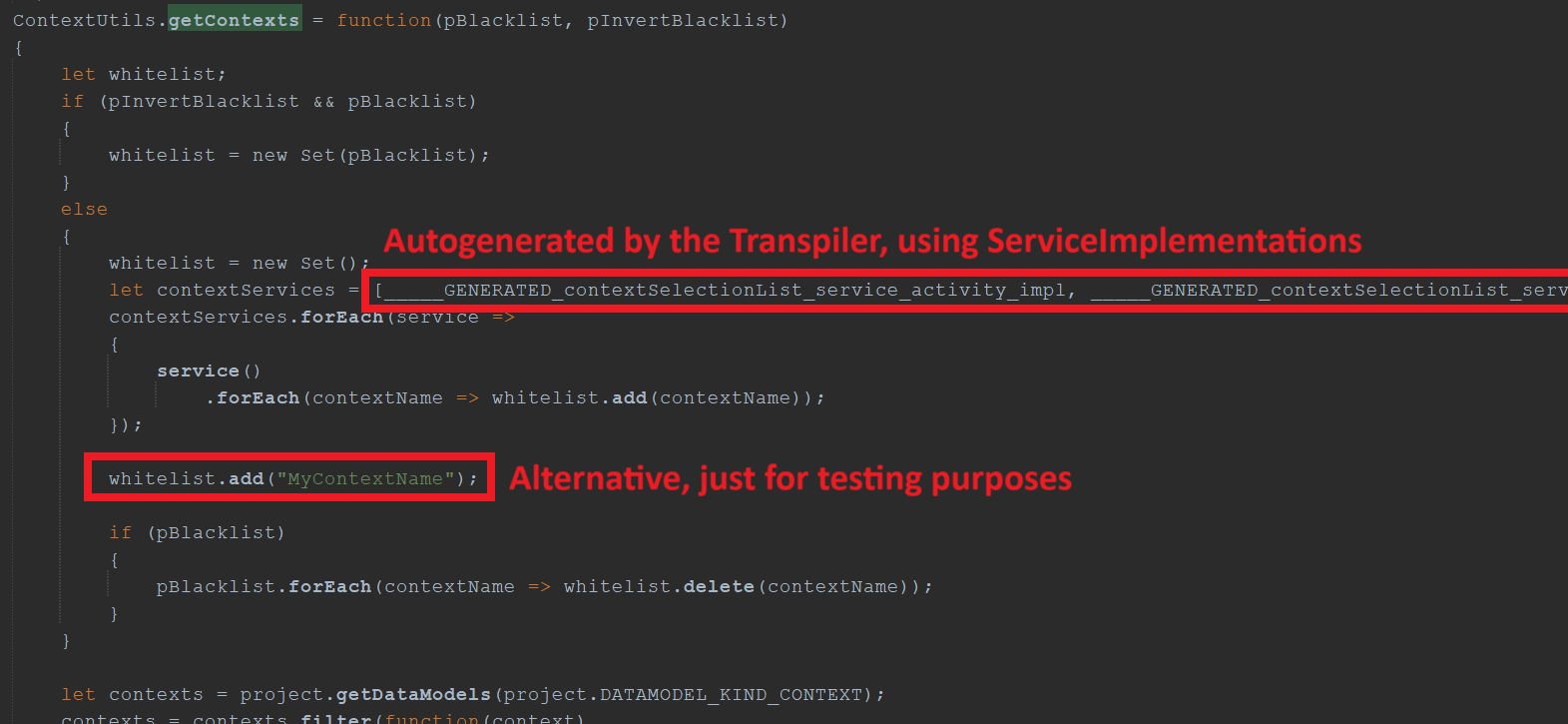
ContextUtils_lib.ContextUtils.getContexts (module root)
Extend getContextConsumer
In ContextUtils_lib (module root), you can find a method named ContextUtils.getContextConsumer, which returns the names of all Consumers that determine the records selectable in the right part of the "Connections" ViewTemplate:
Now, make sure your Context's name and the Consumer's name (see this chapter) is included in the consumerMapping of method ContextUtils.getContextConsumer. When using modularization, you will do this via a ServiceImplementation. Then, the Transpiler will automatically generate the required function (returning a mapping of Context name(s) and Consumer name(s)) in ContextUtils_lib (module root) ...
function _____GENERATED_contextConsumerMapping_service_cm_impl()
{
let implementation = {
"Organisation": "Organisations",
"Person": "Persons",
"PrivatePerson": "PrivatePersons"
};
//@ts-ignore
return implementation;
}
...and automatically add this function to the array of generated functions in method getContextConsumer, which will subsequently be looped over, in order to fill the consumerMapping. (See screenshot below.)
However, for testing purposes (when using an unmodularized project), you may simply add your Context's name and your Consumer's name manually to the consumerMapping:
consumerMapping["MyContextName"] = "MyConsumerName";
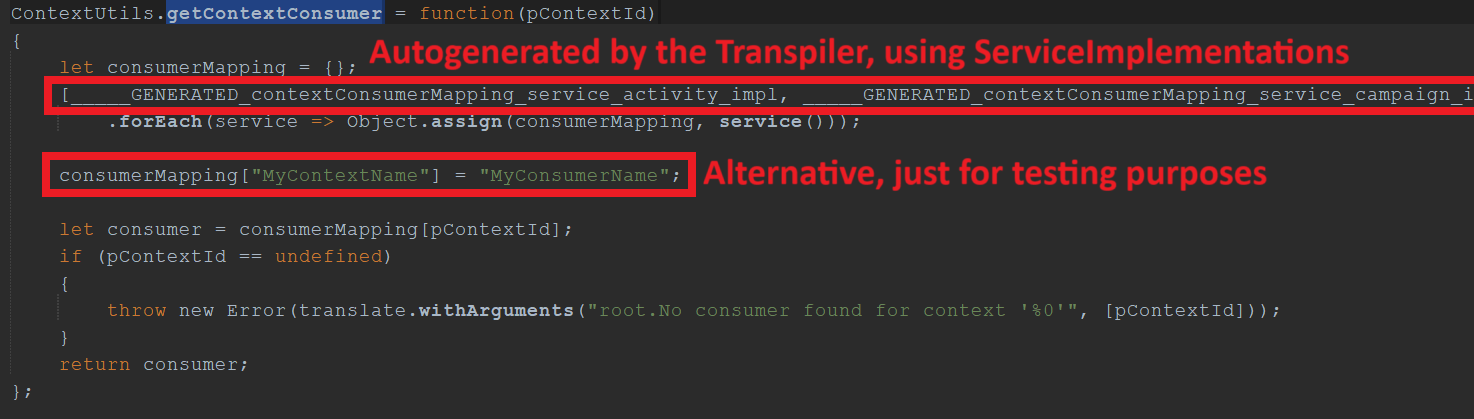
ContextUtils_lib.ContextUtils.getContextConsumer (module root)
Done!
Test
Now, test your customization by selecting any record in the FilterView of your Context, executing new Action "New task" in the PreviewView, creating and saving a task, and then checking, if the new task appears in the MainView's tab "Tasks".