Task
Once you have created the Contexts, Entities, and Views, you can now create the 2 corresponding database tables and connect them with the Entities.
You can find helpful information in chapter The Basics and chapter RecordContainers.
Solution
Database tables
Open the database editor and choose "Create Table..." from the context menu of folder "Tables":
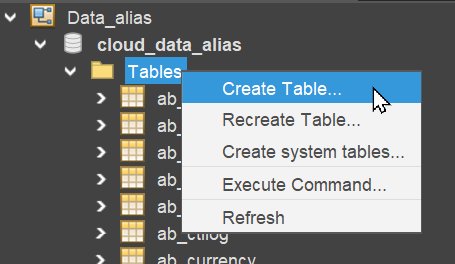
Add the table name and all required columns for both Entities. Leave the predefined default columns ("DATE_NEW" etc.) unchanged. Remember, not to create columns for calculated EntityFields.
Columns holding keywords (e.g., COLOR) are always of data type VARCHAR(36). Column PRICE can be set as DECIMAL(10,2). All columns working as foreign keys are configured with index = true, but without foreign key constraint.
Update of Alias Definition
In the project, update the Alias Definition via alias > Data_alias (double click) > (Navigator:) Data_alias > RMB "Diff Alias <> DB Table" etc.
This makes your new DB tables available in the project.
RecordContainer
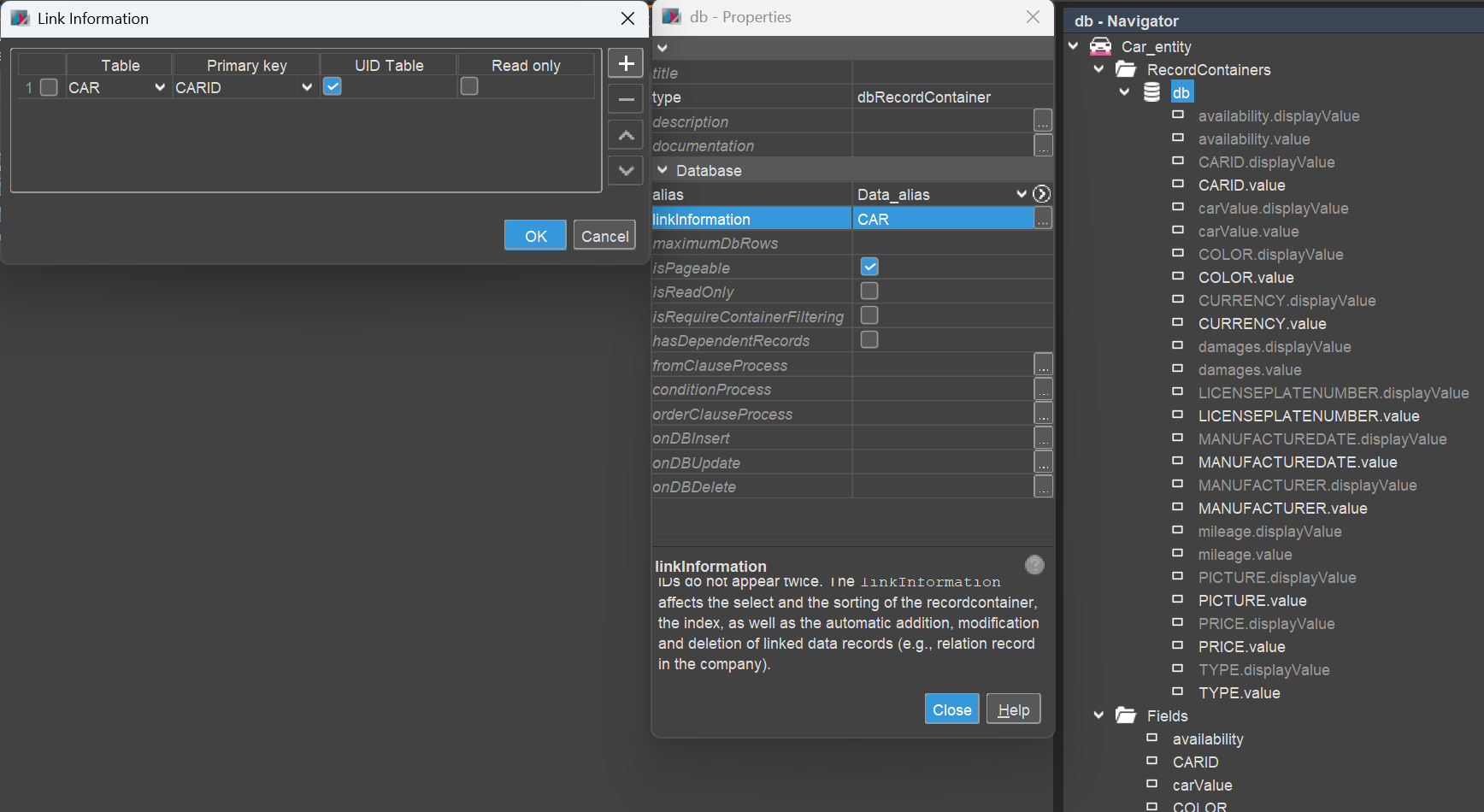
For both Entities, create a Database RecordContainer (dbRecordContainer) by opening the Entity in the Navigator and choosing "New RecordContainer" from the context menu. Set the RecordContainer's properties alias (Data_alias) and linkInformation (tables and primary key) accordingly. Map all (non-calculated) EntityFields to their respective database columns.
The result should look something like this:
Car_entity:
CarDriver_entity:
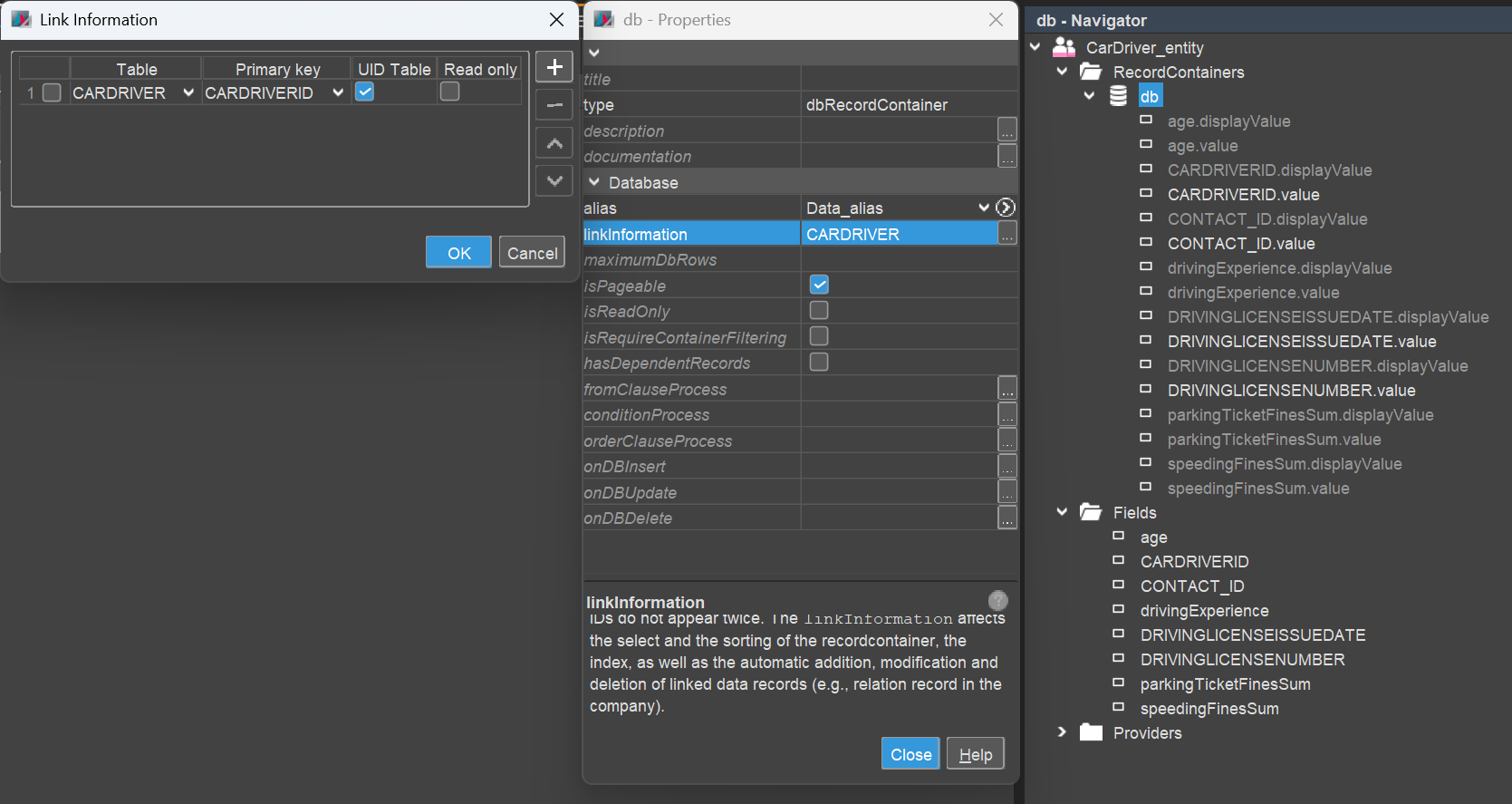
For all EntityFields that should be included as filter criteria, set their RecordFieldMapping's property isFilterable to true.
Deploy and Test
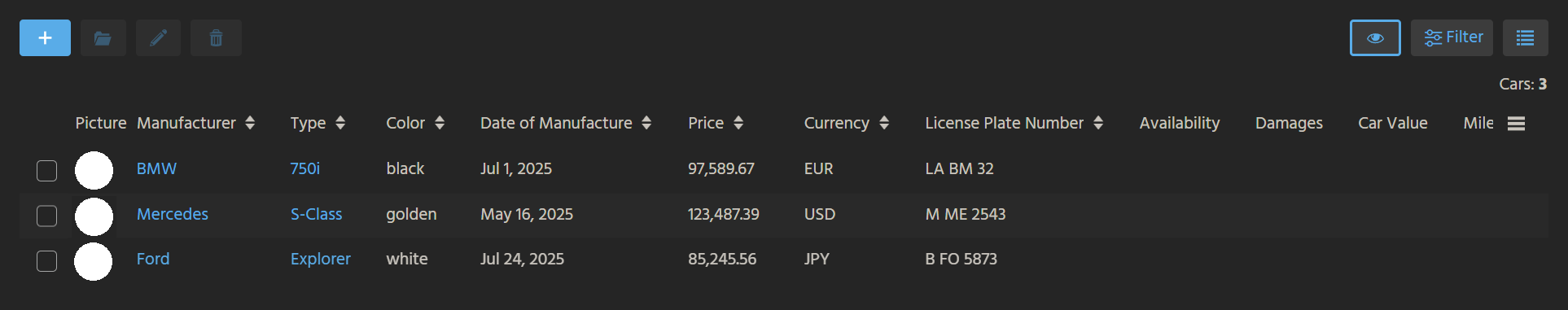
Deploy your changes, open Context Car, and enter some test data.
As for the keyword fields (like CURRENCY) and the foreign key field CONTACT_ID, simply add some data manually. We will enable a selection via dropdown/lookup later.
The result could look like this:
Do the same for Context CarDriver.